- Theory of Career Choice and Development – Anne Roe It’s not my intention to give full information or an extensive discussion on every theory. This website is intended to be a starting point and the main difference with other websites is the visual representation of the theory, which I hope will help get to grips with the theory.
- Anne Roe Career Development Theory Pdf Converter 'Building the Dream Team Workbook' is designed to help an organization not only build but, sustain a dream team to fulfill its mission and vision by writing the vision and making it plain.
PDF, text format, or print directly. Import Current Resumes. Get resume grade and tips to improve. Automatic import to resume builder. Resume & Examples. Europe Q4 2008 Mn65 Map Zip Codes. Roe’s Career Theory. The publication of The Psychology of Occupations would introduce Roe’s theory of personality development and career choice.
1904-1991
Roe's Career Development Theory (1956) is very individually focused:
- Biology
- believed that intelligence and temperament are more determined by heredity than are interests and attitude
- Sociology
- Economic limitations, race, gender, and cultural or social attitudes beyond individual's control
- Career not determined by genetics, more frustrations or satisfactions in life.
- Careers determined by degree of satisfaction being met
- The more intense the needs, the more need to be successful
- Psychology
- Based on the psychological needs that develop from the interaction between child and their parents/caretakers
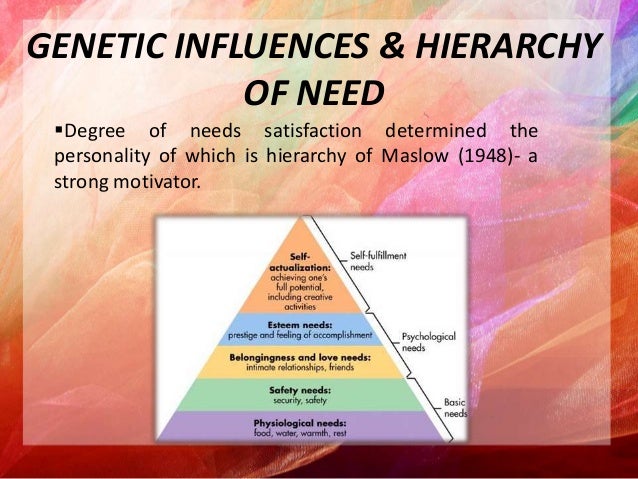
Central to Roe's theory is Maslow's Hierarchy of Needs.
- Physiological needs must be satisfied before other needs can be met
- Safety needs: shelter, good health, avoidance of danger
- occupational needs: security needs come first before other interactions and benefits
- Belonging and love: caring for and being cared for
- Esteem needs: need to feel important and respected
- Information needs: to perform job well
- Understanding: must understand and interpret great amounts of information
- Beauty: in the arts and entertainment field, it is essential
- Self-Actualization: need to be all that one can be (Roe finds this more important than information)
Career Theory
Career Development Theory Super
8 groups- Service
- one person doing something for another person: nurse, health care, counselor
- Business contact
- persuading others: public relations, sales
- Organization
- management: Senator, accountant, secretary
- Technology
- making, producing, maintaining, and transporting products: engineers, pilots, production managers
- Outdoor
- protection of environment, production of crops: farm manager, landscape architect, fish and game officer
- Science
- development of science natural and physical: professor, pharmacist, medical
- General Culture
- interested in human activity and culture: ministry, history, education
- Arts and Entertainment
- performers: music conductor, museum curator, football player, stagehand

Early Parent-Child Relationship (3 categories)
Anne Roe Career Development Theory Pdf To Excel Free
- Concentration on the child
- Overprotective: parent encourages dependance on the parent and restricts curiosity and exploration
- Overdemanding: parent requests perfection from the child, asking for excellent performance and setting high standards of behavior (first born)
- Avoidance of the child
- Rejection: parent may be overly critical of the child or punish the child excessively
- Neglect: ignores the child for many reasons, such as, parents concern with their own problems, other children, or work
- Acceptance of the child
- Parents encourage independence rather than dependence and do not ignore or reject their child, creating a relatively tension free environment
- Casual acceptance: parents have a low-key attitude offering a minimum amount of love
- Loving acceptance: parents offer a warmer attitude toward the child, while not interfering with the child's resources by fostering dependency